Chronic disease development increases with suppression of acute infections diseases in the population – a case controlled pilot study of 166 cases
Dr Seema Mahesh1, Dr Mahesh Mallappa1, Prof George Vithoulkas2
1 Centre for Classical Homeopathy Bangalore India
2 International Academy of Classical Homeopathy, University of the Aegean, Greece
Background:
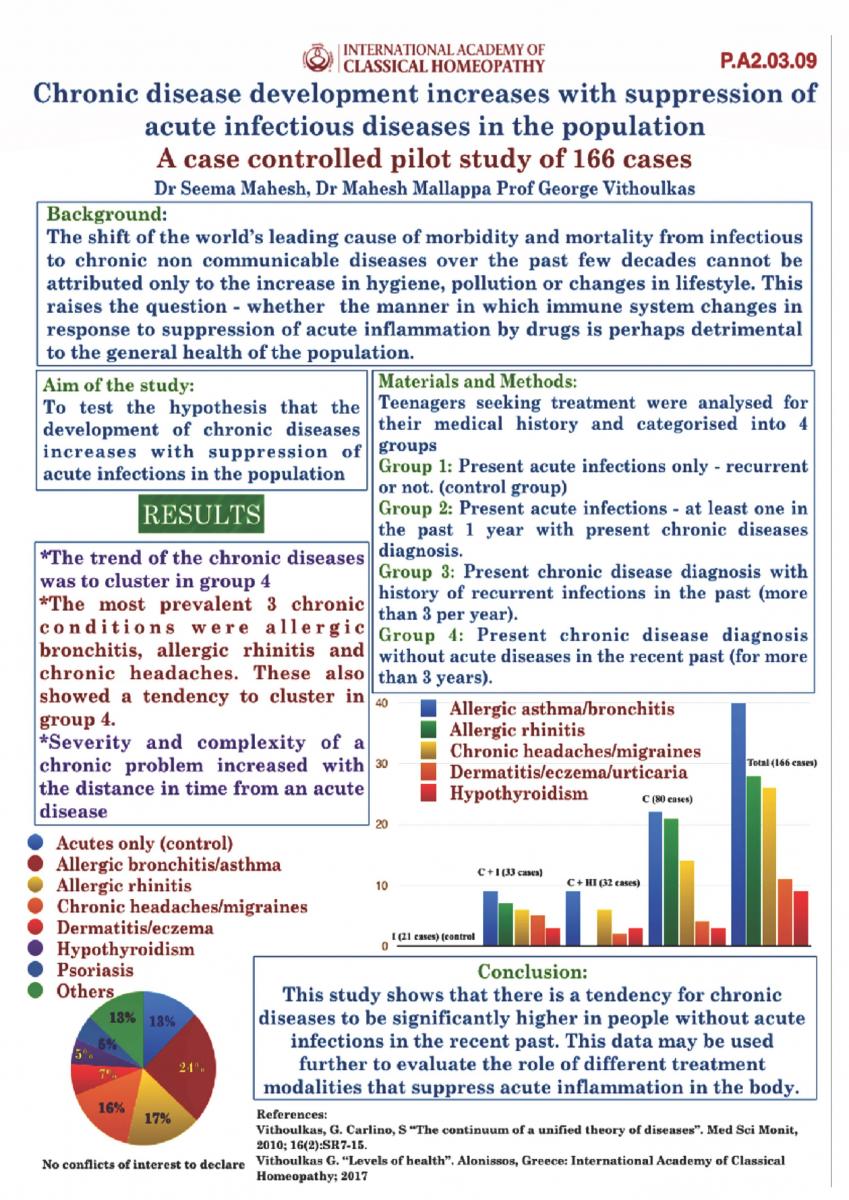
The change of the world’s leading cause of morbidity and mortality from infectious to non communicable diseases over the past few decades cannot be attributed to the increase in hygiene or change in lifestyle alone. This raises the question – whether the manner in which immune system morphs in response to suppression of acute inflammation is detrimental to the general health of the population.
Aim of the study:
To test the hypothesis that the development of chronic diseases increases with suppression of acute infections in the population
Materials and Methods:
Teenagers opting for treatment at Centre For Classical Homeopathy, Bangalore, India were analysed for their medical history and categorised into 4 groups
Group 1: Present acute infections only – recurrent or not. (control group)
Group 2: Present acute infections – at least one in the past 1 year with present chronic diseases diagnosis.
Group 3: Present chronic disease diagnosis with history of recurrent infections in the past.
Group 4: Present chronic disease diagnosis with no history of recurrent infections in the past.
Results:
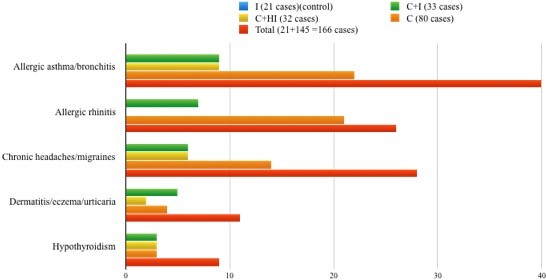
The trend of the chronic diseases was to cluster in group 4
The most prevalent 3 chronic conditions were allergic bronchitis, allergic rhinitis and chronic headaches. These also showed a tendency to cluster in group 4.
Conclusion:
This study shows that there is a tendency for chronic diseases to be significantly higher in people without acute infections. This data may be used further to evaluate the role of different treatment modalities that suppress acute inflammation in the body.
Results:
I: Acute infections only
C + I: Chronic disease diagnosis + Acute infections at present
C + HI: Chronic disease diagnosis with history of acute infections – no acute infections since onset of the chronic disease
C: Chronic disease diagnosis at present with history of acute diseases